Selecting the appropriate material for your application is critical for successful product realization. Chemical compatibility, physical properties, and processing techniques can differ significantly depending on the selection. So, let’s take a look at the differences between common plastic tubing materials for precision fluidics and when to use each.
Considerations for Choosing Plastic Tubing
In general, determining the best material for your plastic tubing needs should include considerations for:
- Working temperature ranges
- Superior ID surface finishes compared to stainless steel tubing
- Chemical compatibility
- Dielectric insulation properties
- Thermal properties
- Strength
- Cost
Materials’ properties can range widely and directly impact the performance and life cycle potential of your application.
Common Plastic Tubing Materials
Known for their superb chemical compatibility, fluoropolymers are a common option in the life science and diagnostic markets. Soft PVC tubing is also a common option in many fluid control and medical applications with a variety of appropriate sterilization methods. Additionally, PEEK is a material with broad chemical compatibility and can withstand higher pressures, finding extensive use in HPLC/UPLC devices. All these materials have USP-VI, REACH, and RoHS compliant resins available, which greatly helps with their implementation in a wide range of applications.
The following are commonly used tubing materials:
- Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
- Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene (FEP)
- Perfluoralkoxy (PFA)
- Poly Ether Ether Ketone (PEEK)
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Materials’ properties can range widely and directly impact the performance and life cycle potential of your application.
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
Material for Tubing

The first step of a successful product is having clear and achievable design requirements. Our engineers will work with you to understand your short- and long-term goals and requirements for your project. Clearly defining the motivation, goals, budget, and market helps to determine the resources and methods appropriate to complete the design.
Benefits of PTFE
Here are a few benefits of PTFE:
- Excellent chemical resistance
- Virtually no water absorption (≤0.01%)
- Working temperature of -454°F to 500°F
- Low coefficient of friction – “non-stick”
- Excellent dielectric insulation properties
Disadvantages of PTFE
Here are a few disadvantages of PTFE:
- Being a thermoset plastic, PTFE is more limited in its ability to be thermoformed
- Cold-flow or “Creep” can be a concern depending on the application (Cold-flow is the phenomenon where a material deforms under sustained pressure, at room temperatures, and is unable to completely return to its original dimensions)
- Not well suited for welding
Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene (FEP)
Material for Tubing
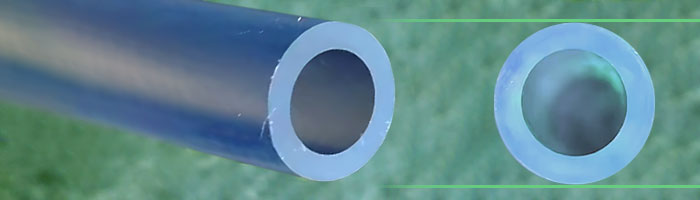
Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene (FEP) is a thermoplastic fluoropolymer—and this material creates opportunities for great flexibility in forming and fabrication techniques. It can be melted and reshaped multiple times, including welding. FEP is also clear, which may be desirable based on the application. Its chemical resistance is excellent, and it enjoys good weathering resistance as well.
Benefits of FEP
Here are a few benefits of FEP:
- Excellent chemical resistance
- Very low water absorption (≤0.03%)
- Greater radiation resistance
- Low coefficient of friction – “non-stick”
- Excellent dielectric insulation properties
Disadvantages of FEP
Here are a few disadvantages of FEP:
- Narrower working temperatures than PTFE or PFA at -328°F to 390°F
- Lowest strength and stiffness of the fluoroplastic materials
Perfluoralkoxy (PFA)
Material for Tubing

Perfluoralkoxy (PFA) was originally developed as a high-temperature version of FEP. PFA is comparable to FEP with higher working temperatures while remaining melt-processable, including welding.
Benefits of PFA
Here are a few benefits of PFA:
- Excellent chemical resistance
- Greater flexibility than PTFE and FEP
- Working temperature of -328°F to 500°F
- Low coefficient of friction – “non-stick”
- Excellent dielectric insulation properties
Disadvantages of PFA
Here are a few disadvantages of PFA:
- More expensive option of the fluoroplastic materials
Poly Ether Ether Ketone (PEEK)
Material for Tubing
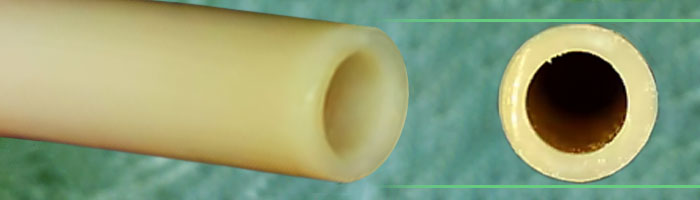
Poly Ether Ether Ketone (PEEK) is a biocompatible material that is commonly used in life science and HPLC applications. It’s common for PEEK to replace stainless steel tubing in high pressure applications where PEEK’s superior chemical compatibility and flexibility is valued over the increase in cost.
Benefits of PEEK
Here are a few benefits of PEEK:
- Great chemical resistance, but will suffer from strong acids (Sulfuric, Aqua Regia, etc.)
- Working temperature of -94°F to 500°F
- Suitable for higher pressures
- Alternative for stainless steel tubing
Disadvantages of PEEK
Here are a few disadvantages of PEEK:
- More expensive than fluoropolymer or PVC tubing
- Least flexible option: cracking can be a concern in use cases with a lot of movement
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Material for Tubing

Soft Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) tubing is an economical solution for many applications. Its chemical resistance isn’t as broad as fluoropolymers, so it is commonly used with less aggressive chemicals in water plumbing, medical tubing, and waste fluid handling.
Benefits of PVC
Here are a few benefits of PVC:
- Clear for easy visualization of flow
- Non-wetting
- EtO, gas, and gamma radiation sterilizable
- Low cost
Disadvantages of PVC
Here are a few disadvantages of PVC:
- Lowest strength of common tubing options
- Lowest working temperature of 165°F
- Least broad chemical resistance
Frequently Asked Questions about Tubing Materials
PVC vs. PFA?
- In applications where chemical interaction and high temperatures are present, PFA is the better option. If you need a low-cost alternative in a simpler environment, then you may want to consider PVC.
PEEK vs. FEP?
- PEEK is the preferred material for general use since it’s affordable and offers a great range of performance benefits. However, FEP should be used if you need flexibility, high temperature resistance, and chemical compatibility.
Have other questions about tubing materials? Get in touch with us!
The Importance of Selecting the Right Tubing Material
Materials’ properties and their operational conditions contribute toward success or failure of a given application in its indented environment.
Careful selection of materials is essential for avoiding financial costs associated with product failures, failing validation, delays in products hitting the market, and potentially long-term loss of reputation that can accompany recalls.
Therefore, it’s critical that proper selection, testing, and prototyping be observed.
Ready to get started? Find the tubing material best for your application.
